- Services
- Artificial Intelligence Development
- Deep Learning & Neural Network Development Services
- Professional Machine Learning Development Services
- Enterprise Computer Vision Development Services
- Enterprise Natural Language Processing Development Services
- Chatbot & Conversational AI Development Services for Business
- Enterprise Computer Vision Solutions For Healthcare
- Transformative Healthcare AI Development
- Retail & E-commerce AI Solutions for Personalization & Growth
- AI Integration & MLOps Development Services
- AI Agent Development & Intelligent Automation
- Generative AI Solutions
- Outsourced Product Development
- Custom Software Development
- Software Customization & Integration
- Mobile App Development
- Custom Application Development
- Software Architecture Consulting
- Enterprise Application Development
- AI-Powered Documentation Services
- Product Requirements Document Services
- Artificial Intelligence Development
- Industries
- Healthcare Software Development
- Telemedicine Software Development
- Medical Software Development
- Electronic Medical Records
- EHR Software Development
- Remote Patient Monitoring Software Development
- Healthcare Mobile App Development Services
- Medical Device Software Development
- Healthcare Mobile App Development Services
- Patient Portal Development Services
- Practice Management Software Development
- Healthcare AI/ML Solutions
- Healthcare CRM Development
- Healthcare Data Analytics Solutions Development
- Hospital Management System Development | Custom HMS & Healthcare ERP
- Mental Health Software Development Services
- Medical Billing & RCM Software Development | Custom Healthcare Billing Solutions
- Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) Development
- Clinical Trial Management Software Development
- Pharmacy Management Software Development
- Finance & Banking Software Development
- Retail & Ecommerce
- Fintech & Trading Software Development
- Online Dating
- eLearning & LMS
- Cloud Consulting Services
- Healthcare Software Development
- Technology
- Products
- About
- Contact Us
ERP vs CRM vs Custom Platform: What Does Your Business Actually Need?

Every growing business eventually faces a critical decision: which software platform will best support operations, customer relationships, and long-term growth? The choice between Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platforms, and custom-built solutions represents one of the most significant technology investments an organization will make.
This comprehensive guide cuts through the marketing noise to help you understand what each solution truly offers, when to choose one over the others, and how to evaluate whether off-the-shelf software or a custom platform aligns with your business objectives. Whether you’re a mid-sized manufacturer considering your first ERP implementation, a sales-driven organization evaluating CRM options, or an enterprise with unique requirements exploring custom development, this article provides the framework for making an informed decision.
The stakes are high. According to industry research, the average cost of an ERP implementation for mid-sized companies ranges from $150,000 to $750,000, while enterprise CRM deployments can reach similar figures. Custom platform development typically requires even larger initial investments but may deliver superior long-term value for organizations with specific needs. Understanding the true capabilities, limitations, and strategic implications of each option is essential before committing significant resources.
Understanding ERP Systems: Integrated Business Management
What is an ERP System?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software integrates core business processes into a unified system, providing a single source of truth for organizational data. Rather than maintaining separate databases for accounting, inventory, human resources, procurement, and manufacturing, an ERP system consolidates these functions into interconnected modules that share information in real-time.
Modern ERP systems evolved from Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP) solutions of the 1980s, expanding beyond production management to encompass virtually every operational aspect of a business. Today’s ERP platforms serve as the digital backbone for organizations ranging from small manufacturers to multinational corporations, enabling process standardization, data consistency, and operational efficiency at scale.
| ERP Module | Primary Functions | Typical Users | Business Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Management | General ledger, accounts payable/receivable, asset management, budgeting, financial reporting | Finance team, controllers, CFO, auditors | Real-time financial visibility, automated reporting, compliance management, audit trails |
| Supply Chain Management | Procurement, inventory control, demand planning, supplier management, logistics | Procurement team, warehouse managers, supply chain directors | Optimized inventory levels, reduced carrying costs, supplier performance tracking |
| Manufacturing/Production | Production planning, shop floor control, quality management, bill of materials, work orders | Production managers, plant supervisors, quality assurance | Improved production scheduling, quality control, reduced waste, capacity planning |
| Human Resources | Personnel management, payroll, benefits administration, time tracking, talent management | HR team, managers, employees, payroll administrators | Streamlined HR processes, compliance tracking, employee self-service, workforce analytics |
| Sales & Distribution | Order management, pricing, shipping, invoicing, sales analysis | Sales team, customer service, order fulfillment | Faster order processing, improved accuracy, integrated fulfillment, sales visibility |
| Project Management | Project planning, resource allocation, time tracking, budgeting, milestone tracking | Project managers, team members, resource managers | Resource optimization, project profitability analysis, timeline management |
ERP Software Comparison: Leading Platforms
The ERP market is dominated by several major vendors, each offering distinct capabilities, pricing models, and industry specializations. Understanding the competitive landscape is essential for effective ERP software comparison.
| ERP Platform | Best Suited For | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| SAP S/4HANA | Large enterprises, global operations, complex requirements | Comprehensive functionality, powerful analytics, industry-specific solutions, proven scalability | High implementation costs, complex customization, steep learning curve, long deployment timelines |
| Oracle NetSuite | Growing businesses, multi-subsidiary organizations, cloud-first companies | True cloud architecture, flexible customization, unified platform, strong financial management | Can become expensive as you scale, limited offline capabilities, customization complexity |
| Microsoft Dynamics 365 | Microsoft-centric organizations, mid-market companies, mixed deployment needs | Microsoft ecosystem integration, familiar user interface, flexible deployment options, AI capabilities | Module fragmentation, integration complexity between components, varying feature maturity |
| Infor CloudSuite | Industry-specific needs, manufacturing focus, mid-to-large enterprises | Deep industry expertise, modern interface, strong manufacturing capabilities, industry templates | Smaller market presence, variable implementation partner quality, less ecosystem support |
| Odoo | Small-to-medium businesses, budget-conscious organizations, phased implementations | Modular approach, open-source option, affordable pricing, extensive app marketplace | Limited scalability for large enterprises, variable module quality, less sophisticated than tier-one solutions |
When ERP Makes Strategic Sense
ERP systems deliver maximum value when your business requires integrated operational management across multiple departments with standardized processes. Consider ERP if you struggle with data silos, manual reconciliation between systems, inventory visibility issues, or lack real-time financial reporting. Manufacturing, distribution, and multi-location retail organizations typically gain the most immediate benefits from ERP implementation.
Understanding CRM Systems: Customer-Centric Operations
What is a CRM System?
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software focuses on managing and optimizing customer interactions throughout the entire customer lifecycle—from initial lead generation through sales conversion, onboarding, ongoing support, and retention. Unlike ERP systems that manage internal operations, CRM platforms are externally focused, designed to improve customer acquisition, satisfaction, and lifetime value.
Modern CRM solutions extend far beyond contact management databases. They encompass sales force automation, marketing automation, customer service management, analytics and reporting, and increasingly, artificial intelligence-powered insights that predict customer behavior and recommend optimal engagement strategies.
| CRM Component | Core Capabilities | Primary Users | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales Automation | Lead tracking, opportunity management, pipeline visualization, forecasting, quote generation, mobile access | Sales representatives, sales managers, sales operations | Shorter sales cycles, improved win rates, accurate forecasting, increased rep productivity |
| Marketing Automation | Campaign management, email marketing, lead scoring, segmentation, landing pages, multi-channel orchestration | Marketing team, demand generation, content marketers | Higher quality leads, improved conversion rates, marketing ROI measurement, personalization at scale |
| Customer Service | Case management, knowledge base, service level agreements, omnichannel support, self-service portals | Support agents, service managers, customer success teams | Faster issue resolution, improved customer satisfaction, reduced support costs, proactive service |
| Analytics & Reporting | Dashboards, custom reports, predictive analytics, performance metrics, customer insights, attribution modeling | Executives, managers, analysts, operations teams | Data-driven decision making, performance visibility, trend identification, strategic planning |
| Partner Management | Partner portal, deal registration, co-marketing, channel analytics, incentive management | Channel managers, partner account managers, indirect sales | Improved partner engagement, channel visibility, streamlined collaboration, reduced channel conflict |
CRM vs Custom System: Leading CRM Platforms
The CRM market offers diverse options ranging from specialized point solutions to comprehensive customer experience platforms. When evaluating CRM vs custom system alternatives, understanding the capabilities and trade-offs of major CRM vendors is essential.
| CRM Platform | Ideal Use Cases | Key Advantages | Notable Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salesforce | Enterprise sales teams, complex sales processes, extensive customization needs | Most comprehensive ecosystem, powerful customization, extensive integrations, industry solutions, proven scalability | Premium pricing, complexity can be overwhelming, requires skilled administrators, customization costs add up |
| HubSpot | Small-to-medium businesses, inbound marketing focus, unified marketing and sales teams | Intuitive interface, excellent free tier, strong marketing capabilities, integrated approach, good support | Limited customization compared to Salesforce, can become expensive at scale, reporting limitations |
| Microsoft Dynamics 365 | Microsoft shops, integration with Office 365, organizations wanting CRM and ERP connection | Deep Microsoft integration, familiar interface, AI capabilities, flexible deployment, unified data platform | Complexity of licensing, implementation challenges, learning curve despite familiar interface |
| Zoho CRM | Cost-conscious businesses, multi-channel sales, international organizations | Affordable pricing, comprehensive features, extensive app ecosystem, multi-language support | Less polished interface, steeper learning curve, integration quality varies, limited enterprise features |
| Pipedrive | Small sales teams, straightforward sales processes, ease-of-use priority | Simple and intuitive, visual pipeline, mobile-friendly, quick implementation, good value | Limited features beyond sales, not suitable for complex processes, basic reporting, less scalable |
When CRM Drives the Greatest Impact
CRM systems deliver optimal ROI for sales-driven organizations where customer relationships directly impact revenue. If your business struggles with lead follow-up, lacks sales pipeline visibility, experiences customer retention challenges, or needs to align marketing and sales efforts, CRM implementation should be a priority. Service-based businesses, SaaS companies, and organizations with complex sales cycles typically see the fastest returns from CRM investments.
Custom Platform Development: Tailored Solutions for Unique Needs
The Case for Custom Software
Custom platform development involves building software specifically designed for your organization’s unique requirements, workflows, and competitive differentiators. Rather than adapting business processes to fit pre-packaged software, custom solutions adapt to your business, potentially delivering competitive advantages that off-the-shelf systems cannot provide.
The decision between CRM vs custom system, or ERP vs custom development, ultimately hinges on whether your business requirements are unique enough to justify custom investment, whether existing solutions truly address your needs, and whether you have the resources to support long-term custom platform ownership.
| Custom Development Scenario | Typical Characteristics | Custom Solution Benefits | Alternative Approaches |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unique Business Model | Novel service delivery, proprietary processes, competitive differentiation through operations | Software aligns precisely with business model, supports unique workflows, protects competitive advantages | Extensive configuration of flexible platform, multiple integrated point solutions |
| Industry-Specific Requirements | Regulated industry with unique compliance needs, specialized terminology, uncommon workflows | Built-in compliance, industry-specific features, optimized for sector requirements | Industry-specific ERP/CRM variant, extensive customization of general platform |
| Complex Integration Needs | Multiple legacy systems, unusual data formats, specialized equipment interfaces | Custom integration architecture, optimized data flow, unified user experience | Integration platform as a service (iPaaS), custom middleware, API development |
| Scalability Beyond Standard Limits | Extreme transaction volumes, unique performance requirements, massive data sets | Optimized architecture for specific needs, custom performance tuning, specialized databases | Enterprise tier of commercial software, architectural optimization, database tuning |
| IP Protection Requirements | Proprietary algorithms, sensitive methodologies, competitive intelligence concerns | Complete control over code and algorithms, proprietary functionality, intellectual property security | Highly configurable platform with proprietary extensions, on-premise deployment of commercial software |
Custom Platform Development Approaches
Organizations pursuing custom development have several architectural approaches to consider, each offering different balances of flexibility, speed to market, and long-term maintainability.

Custom Development Pitfalls to Avoid
Many custom development projects fail or significantly exceed budgets due to common mistakes: underestimating total cost of ownership, inadequate requirements definition, insufficient technical expertise, lack of change management planning, and failure to plan for long-term maintenance. Before pursuing custom development, ensure you have realistic budget expectations, clear requirements, skilled technical resources (internal or partner), and commitment to ongoing platform evolution. Custom software is not a one-time project but an ongoing asset requiring continuous investment.
Head-to-Head Comparison: ERP vs CRM vs Custom Platform
Direct Feature and Capability Comparison
Understanding how these solutions compare across critical dimensions helps clarify which option aligns with your organizational priorities and constraints.
| Comparison Dimension | ERP Systems | CRM Systems | Custom Platforms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Internal operations, process integration, resource management | Customer relationships, sales processes, marketing automation | Whatever business needs require, typically unique or specialized functions |
| Implementation Timeline | 6-18 months for mid-sized; 18-36 months for enterprise | 1-6 months for basic; 6-12 months for comprehensive | 6-24 months depending on scope and complexity |
| Typical Initial Investment | $150K-$750K (mid-market); $1M-$10M+ (enterprise) | $10K-$200K (depending on size and platform) | $200K-$2M+ (varies dramatically by scope) |
| Annual Operating Costs | 15-25% of software costs plus infrastructure | Subscription fees ($50-$300/user/month typical) | 20-40% of development costs for maintenance and evolution |
| Flexibility & Customization | Moderate; configuration within platform constraints | Good; extensive configuration and marketplace extensions | Excellent; unlimited flexibility within technical constraints |
| Scalability | Excellent; proven at enterprise scale | Excellent; cloud platforms scale effectively | Variable; depends on architectural decisions |
| Integration Capabilities | Strong; pre-built connectors for common systems | Excellent; extensive API ecosystem and integrations | Excellent; can integrate with any system given resources |
| User Adoption Complexity | High; significant training required, workflow changes | Moderate; intuitive interfaces but process changes needed | Variable; can be optimized for users or complex |
| Vendor Lock-in Risk | High; difficult and expensive to switch | Moderate to High; data export possible but switching painful | Low; you own the code but dependent on development partner |
| Ongoing Innovation | Vendor-driven; quarterly/annual updates | Vendor-driven; frequent platform improvements | Organization-driven; you control roadmap and priorities |
| Risk Profile | Moderate; proven technology but implementation risks | Low; well-understood implementations, quick time-to-value | High; development risk, requirements risk, execution risk |
Business Scenario Recommendations
Different business situations call for different solutions. This framework maps common scenarios to recommended approaches.
| Business Scenario | Recommended Approach | Rationale | Alternative Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Growing manufacturer with manual processes | ERP implementation | Manufacturing requires integrated inventory, production, and financial management that ERP provides | Custom if processes are highly specialized and provide competitive advantage |
| B2B SaaS company scaling sales team | CRM platform | Sales process management and pipeline visibility are critical; CRM purpose-built for this | Custom if sales process is radically different or integration needs are extreme |
| Retail chain with multiple locations | ERP with retail focus | Need integrated POS, inventory, purchasing, and financial management across locations | Industry-specific ERP may offer better retail functionality than general platform |
| Professional services firm tracking utilization | ERP with project module or CRM with services features | Need both client relationship management and project/resource tracking | Integrated CRM/PSA platform may be more suitable than separate systems |
| Healthcare provider with unique workflows | Custom platform or specialized vertical solution | Compliance requirements and specialized workflows often require custom approach | Healthcare-specific ERP/CRM if workflows align with industry standards |
| E-commerce business with standard operations | Integrated e-commerce platform with ERP connection | E-commerce platforms provide specialized functionality; ERP integration handles back-office | Full ERP if significant offline/wholesale operations exist alongside e-commerce |
| Financial services with proprietary products | Custom platform | Unique product structures and regulatory requirements often require custom solutions | Vertical-specific software if products align with industry standards |
| Startup with limited budget and rapid growth | Best-of-breed cloud tools with strong integration | Cloud CRM + accounting software + point solutions offer flexibility without huge investment | Plan for potential future consolidation into ERP as you scale and standardize |
Cost Analysis and ROI Considerations
Total Cost of Ownership Comparison
Understanding the true cost of each option requires looking beyond initial purchase price to encompass implementation, customization, training, ongoing support, and evolution costs over a 5-year period.
| Cost Component | ERP Systems | CRM Systems | Custom Platforms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software Licensing | $50K-$500K+ (perpetual) or $100-$300/user/month (SaaS) | $50-$300/user/month; free to $5K/month for SMB plans | $0 (you own it) but development costs are higher |
| Implementation Services | $100K-$1M+ (2-5x software cost common) | $10K-$200K depending on complexity | $200K-$2M+ depending on scope |
| Customization | $50K-$500K (often required for competitive advantage) | $10K-$100K (less common but sometimes needed) | Included in development (you build what you need) |
| Data Migration | $25K-$200K depending on legacy system complexity | $5K-$50K (typically simpler than ERP) | $20K-$150K (you control migration approach) |
| Training & Change Management | $25K-$150K (critical for ERP success) | $5K-$30K (CRM typically more intuitive) | $10K-$75K (custom UI can be optimized or complex) |
| Infrastructure (5 years) | $50K-$300K on-premise; included in SaaS pricing | Typically included in SaaS subscription | $75K-$400K (cloud hosting, monitoring, security) |
| Annual Maintenance | 18-22% of software cost (support & updates) | Included in subscription pricing | 20-40% of development cost (bugs, updates, enhancements) |
| Internal Resources (5 years) | $300K-$750K (admin, power users, support) | $150K-$400K (admin and super users) | $400K-$1M+ (technical staff or ongoing development partner) |
| 5-Year Total Cost (Typical Mid-Market) | $800K-$3M | $300K-$1M | $1M-$4M |
Hidden Costs to Consider
Beyond obvious line items, factor in these often-overlooked costs: productivity loss during transition, opportunity cost of delayed implementation, costs of maintaining parallel systems during migration, expenses of failed user adoption requiring remediation, and the cost of future platform evolution as your business changes. Organizations frequently underestimate these soft costs by 30-50%, leading to budget overruns and disappointment.
ROI Expectations and Timelines
Return on investment varies dramatically based on implementation quality, organizational readiness, and how well the chosen solution aligns with actual business needs.
| Solution Type | Time to Positive ROI | Primary ROI Drivers | Realistic Success Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| ERP Systems | 18-36 months | Process efficiency, inventory optimization, reduced manual work, better decision making | 15-25% inventory reduction, 20-30% faster financial close, 30-40% reduction in manual data entry |
| CRM Systems | 6-18 months | Increased sales productivity, higher conversion rates, improved retention, marketing efficiency | 10-20% increase in sales productivity, 5-15% improvement in conversion rate, 25-35% better lead management |
| Custom Platforms | 12-36 months | Competitive differentiation, process optimization, unique capabilities enabling new business models | Variable by business case; should deliver capabilities impossible with commercial software |
Decision Framework: Choosing the Right Path
The ERP vs CRM Decision
Many organizations face the fundamental question: should we implement ERP or CRM first? The answer depends on where your most pressing pain points and opportunities lie.
Choose ERP First When:
- Your most significant challenges are operational: inventory management, financial visibility, production efficiency, supply chain coordination
- You struggle with data consistency across departments and need a single source of truth for operational data
- Manual processes and disconnected systems create inefficiency, errors, and delays in core business operations
- Financial reporting takes too long, lacks accuracy, or doesn’t provide needed visibility for decision-making
- You’re in manufacturing, distribution, or other operations-intensive industries where ERP delivers immediate value
- Compliance requirements demand better process control and audit trails across operational systems
Choose CRM First When:
- Revenue growth is the primary goal and improving sales effectiveness would have the most immediate impact
- You lack visibility into your sales pipeline, struggle with lead management, or have inconsistent sales processes
- Customer retention is suffering due to poor service management or lack of customer interaction history
- Marketing and sales are not aligned, leading to wasted marketing investment and missed opportunities
- Your business is sales-driven (consulting, SaaS, professional services) where customer relationships are the core asset
- You have relatively simple back-office operations that don’t require comprehensive ERP functionality
The Custom Development Decision Matrix
Determining whether custom development makes sense requires honest assessment across multiple dimensions. Use this framework to evaluate the custom platform option.
| Evaluation Criteria | Favor Commercial Software | Consider Custom Development |
|---|---|---|
| Process Uniqueness | Your processes align with industry standards and best practices | Your processes are highly unique and provide competitive differentiation |
| Budget Availability | Limited capital budget; need to minimize upfront investment | Significant budget available for initial development and ongoing evolution |
| Technical Capability | Limited internal technical expertise or development resources | Strong technical team internally or reliable development partner relationship |
| Timeline Pressure | Need solution quickly; urgent business requirements | Can invest 12-24 months for initial deployment; long-term thinking |
| Risk Tolerance | Low risk tolerance; need proven, reliable solution | Higher risk tolerance; willing to accept development uncertainties |
| Industry Maturity | Mature industry with well-defined processes and available vertical solutions | Emerging industry or unique business model without suitable commercial options |
| Integration Complexity | Standard integration needs that commercial platforms handle well | Complex, unusual integration requirements with legacy or specialized systems |
| Scalability Requirements | Growth expectations within capabilities of commercial platforms | Unique scalability needs that commercial solutions don’t address effectively |
| Strategic Importance | Software is enabling technology but not source of competitive advantage | Software capabilities are core to business strategy and differentiation |
Implementation Considerations and Success Factors
Critical Success Factors Across All Options
Regardless of whether you choose ERP, CRM, or custom development, certain factors consistently determine implementation success or failure.
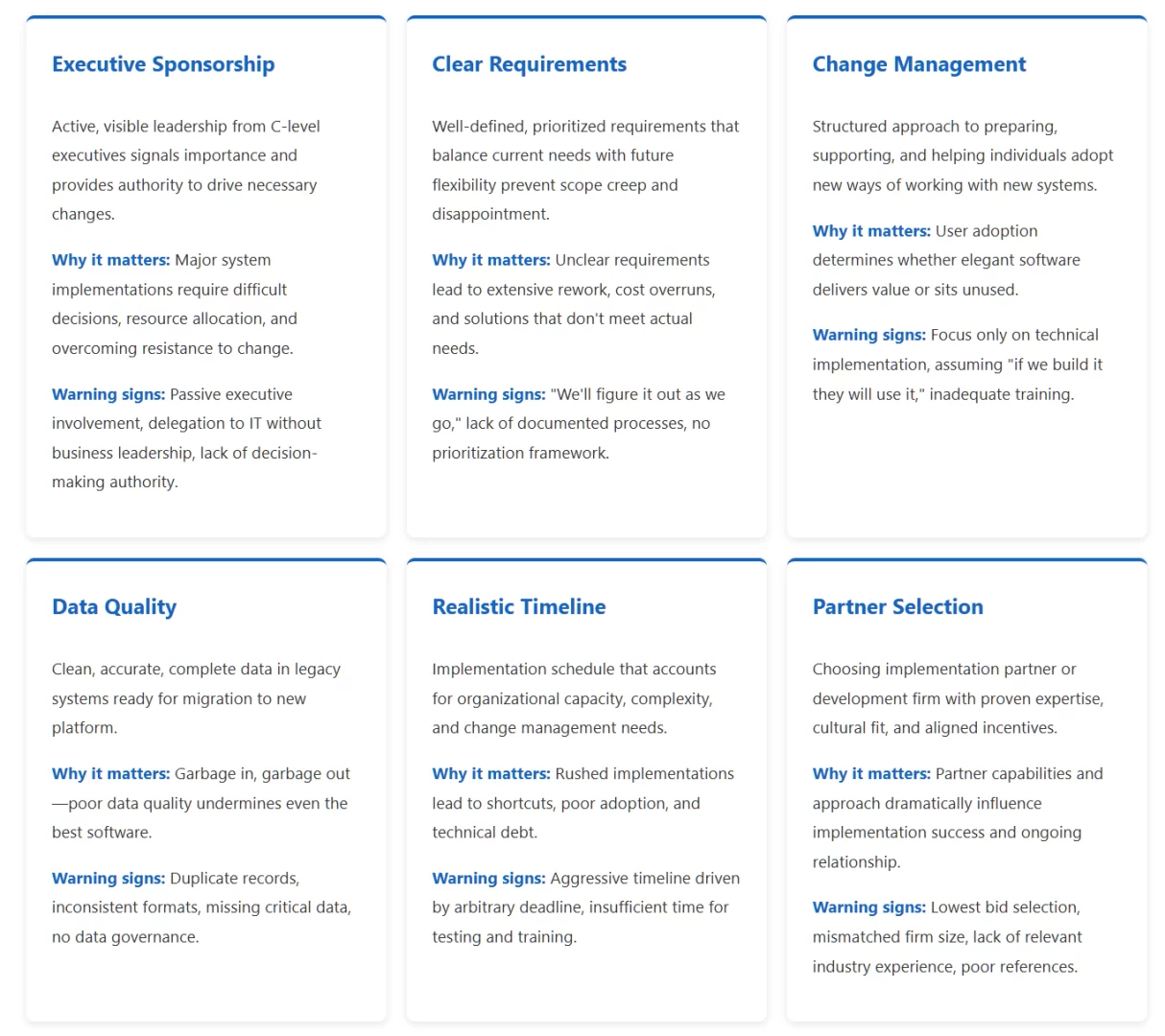
Common Implementation Pitfalls
Learn from others’ mistakes. These pitfalls appear repeatedly across failed or troubled implementations.
Top 10 Implementation Mistakes
- Underestimating total cost by 40-60%, especially ongoing costs and internal resources required
- Over-customizing commercial software to match every existing process rather than adapting processes
- Insufficient testing before go-live, leading to critical issues discovered in production
- Inadequate training leaving users unable to effectively use the system
- Scope creep continuously adding features and requirements without adjusting timeline or budget
- Poor data migration planning causing errors, duplicates, and missing information in the new system
- Ignoring integration requirements until late in the project when they prove more complex than expected
- Treating as IT project rather than business transformation requiring cross-functional leadership
- No post-implementation support plan leaving users struggling after go-live
- Failure to measure ROI meaning you never know if the investment delivered expected value
Conclusion and Recommendations
Key Takeaways: ERP vs CRM vs Custom Platform
The choice between ERP, CRM, and custom platform development is not one-size-fits-all but depends on your specific business situation, priorities, constraints, and strategic objectives.
Final Decision Guidelines
- Choose ERP when operational efficiency, process integration, and financial visibility are your primary needs. ERP delivers maximum value for manufacturing, distribution, and operations-intensive businesses.
- Choose CRM when revenue growth through improved sales effectiveness, marketing alignment, and customer relationship management is the priority. CRM excels for sales-driven, service-oriented organizations.
- Choose Custom Development when your requirements are truly unique, commercial solutions cannot deliver needed capabilities, and you have the budget, timeline, and technical resources to support custom platform ownership.
- Consider Hybrid Approach using commercial software for commodity functions while building custom components for competitive differentiators. This balances speed, cost, and flexibility.
- Don’t Choose Based Solely on Cost—the cheapest initial option often becomes most expensive through poor fit, extensive customization, or replacement costs.
Remember that this decision has long-term implications. The software you implement today will likely serve your organization for 5-10 years, shaping how you work, what’s possible, and how quickly you can respond to market changes. Take the time to thoroughly evaluate your options, involve key stakeholders, and choose a solution that not only solves today’s problems but positions you for future success.
Questions to Ask Before Making Your Decision
Self-Assessment Checklist
- What are our top three business pain points or opportunities that software should address?
- Do our processes align with industry standards, or are they uniquely competitive advantages?
- What is our realistic budget for initial implementation and ongoing operation (5-year view)?
- How quickly do we need a solution, and what’s driving that timeline?
- What internal resources (people, time, expertise) can we dedicate to this initiative?
- How important is proven, low-risk technology versus cutting-edge capabilities?
- Will our chosen solution integrate with our existing systems, or do we need to replace them too?
- Are we prepared to change our processes to match software best practices?
- What happens to our business if this implementation fails or significantly delays?
- Do we have executive commitment and organizational readiness for significant change?
Your answers to these questions will guide you toward the solution that best fits your situation. There is no universally “best” choice—only the best choice for your specific circumstances, objectives, and constraints.
Expert Guidance for Your Software Decision
Choosing between ERP, CRM, and custom platform development is one of the most important technology decisions your organization will make. Artezio helps businesses navigate this complexity with expert consulting, objective assessment, and implementation excellence.
Our Software Strategy Services Include:
- Comprehensive needs assessment and requirements definition to clarify what you actually need
- ERP software comparison and vendor evaluation based on your specific requirements
- CRM vs custom system analysis with objective recommendations
- Custom platform development for organizations with unique requirements
- Implementation services for ERP, CRM, and custom solutions
- Integration architecture design connecting disparate systems into cohesive platforms
- Change management support ensuring successful user adoption
- Post-implementation optimization and ongoing platform evolution
Recent Posts
- The Foundation Crisis: Why Hiring AI Specialists Before Data Engineers is Setting Companies Up for Failure
- ERP vs CRM vs Custom Platform: What Does Your Business Actually Need?
- The AI Enthusiasm Gap: Bridging Corporate Optimism with Public Skepticism in Enterprise AI Adoption
- The Future of AI-Powered Development: How Cursor Plans to Compete Against Tech Giants
- How Much Does Custom Software Development Cost in 2025? Real Numbers & Breakdown

